NRNP 6665 Week 8 Assignment Study Guide Forum Example Study Guide Forum
NRNP 6665 Week 8 Assignment Study Guide Forum Example
Study Guide Forum
Learning disorders are neurological conditions that interfere with the ability to acquire or use academic skills such as reading, writing, and mathematics. The DSM-5-TR categorizes them under specific learning disorders, highlighting significant discrepancies between an individual’s learning ability and their age- appropriate skills.
I. Definition and Core Features
Learning Disorders refer to ongoing problems in academic tasks such as reading (dyslexia), writing (dysgraphia), or mathematics (dyscalculia).
Symptoms appear during the formal schooling period and tend to persist into adulthood.
Signs include unexpected underachievement and frustration in specific areas, despite normal intelligence or adequate educational opportunities.
Refer to DSM-5-TR criteria for standard diagnostic guidelines (American Psychiatric Association, 2022).
II. Signs and Symptoms (DSM-5-TR)
Difficulty interpreting letters or words, or difficulty with spelling and grammar.
Persistent errors in computation or calculation.
Slow reading speed or poor reading comprehension. Written expression challenges, including poor grammar, punctuation, or paragraph organization.
III. Differential Diagnosis
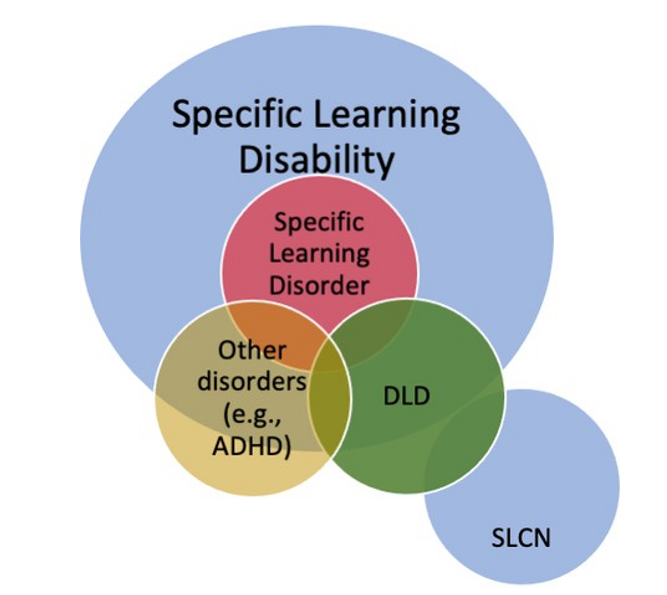
Intellectual Disability: Global cognitive delays, rather than isolated academic deficits.
ADHD: Inattention or hyperactivity that affects academic work but is not limited to learning areas.
Sensory Impairments: Hearing or vision problems that affect academic tasks.
Autism Spectrum Disorder: Broad social and communication challenges that may overlap with learning issues.
IV. Incidence
Prevalence varies according to region and educational systems. Reading- related challenges (dyslexia) are the most frequent subtype (Shaywitz & Shaywitz, 2020).
V. Development and Course
Issues often appear in elementary school when academic demands increase. Some individuals develop better coping strategies, but functional difficulties can linger in adulthood.
VI. Prognosis
Long-term outcomes can be positive with targeted interventions, support services, and accommodations. Early detection and ongoing remediation influence success in academic and workplace settings (Vogel & Reder, 2020).
VII. Culture, Gender, Age Considerations
Cultural differences in language and writing systems may affect
how learning disorders are present.
Males are more frequently identified, but this may reflect referral bias. Early recognition in young children increases the likelihood of beneficial outcomes.
References
First, M. B. (Ed.). (2022). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5-TR. American Psychiatric Association Publishing.
